
Innovation and Design Thinking (Photo Credit: welingkarexed)
I participated in a day-long workshop titled “Innovation and Design Thinking” with Suren Saini organized by b-Academy, and the learning partner was Talent Elevators. I would love to share my learnings and takeaways from this workshop. So let’s start…
About b-academy:
b-academy is a program run by the HR department of bKash Ltd. for its full time-employees only. It offers several technical, non-technical, hard skill, and soft skill learning workshops for bKash employees.
About Instructor:
Suren Saini - India’s Most Practiced Sales Trainer, Leadership Coach, TEDx Speaker, Actor, Model
What is Innovation and Design Thinking?
Innovation:
In simple terms, innovation means the introduction of something new. It can be a completely new thing or can be adding a new creative idea into an existing thing.
Types of Innovation:
- Idea + Logic: At the beginning of thinking we should just avoid logic in our thinking.
- Idea + craziness: At the beginning with idea there should be some craziness too. So that our idea can be widely covered.
Design Thinking:
Design thinking is the process of solving and creating problems. But while solving the problems, design thinking helps to focus on the user needs by balancing business goals and technical feasibility also.
3 Major Skills for Professional Growth:
- Analyze situations and scenarios
- Make logical and timely decisions
- Proactive and user friendly solutions of problem
Practicing and following design thinking principles helps us to active these skills gradually.
Pre-requisite of Design Thinking Process:
- Unlocking/unblocking: Don’t be locked or blocked in a single point. Also don’t be biased by someone or something. Try to think differently in a different way.
- Action oriented: Don’t just think; be action-oriented also. Make it a thinking-plus-trying approach.
- Splitting problem: Split a large problem into smaller and granular ones. Because a small thing is easier to solve than a larger one.
- User centric: Always keep the user or customer in your mind while designing or solving a problem.
- Consider problem as possibility: Don’t see problems in problems. Define the problem and try to solve it without finding any other problem in it.
Design Thinking Framework:
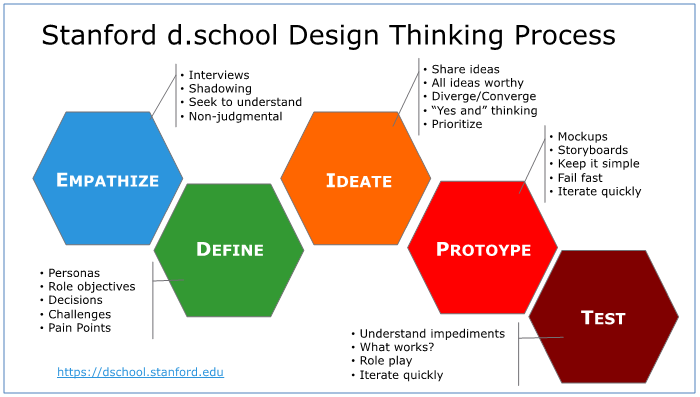
Framework of Innovation and Design Thinking (Photo Credit: theagileelephant)
Empathize: Observe and engage with users and immerse yourself to uncover their needs. The way of how to approach the challenge. Some steps can be followed, like
- Follow user journey map: Understanding process/product, user goals, touchpoints & concerns, user/customer thoughts, overall customer/user experience, and improvement opportunities.
Define: Way of unpacking and synthesizing your empathy findings into compelling needs and insights, and scoping a specific and meaningful challenge. The way of how to interpret findings meaningfully and fruitfully. Some steps can be followed, like
- 5 Why technique: Asking 5 “why” questions to justify the scenario and decisions. Like why this, why those, why and why not, etc.
Ideate: The process in which you aim to generate radical design alternatives. Mentally it represents a process of “going wide” in terms of concepts and outcomes—it is a mode of “flaring” rather than “focusing.” Step beyond obvious solutions and try and harness collective perspectives. Some steps can be followed, like
- Use a mind map: Instead of listing, use the mind map art technique and use large paper. Brainstorm with the team or individually, and then try it one by one.
- Six thinking hats technique: Hats define different thinking approaches and philosophies.
- White hat: Considering only facts and figures.
- Red hat: Express the feeling and emotions.
- Black hat: Consider the negatives of the current scenario.
- Yellow hat: Only consider the positives of the current scenario.
- Green hat: Propose the solutions by creative thinking.
- Blue hat: Summarize and conclude.
So when you ideate, try to wear (meaning consider different scenarios) each hat and find the best possible outcome.
Prototype: Prototyping is getting ideas and explorations out of your head and into the physical world. A prototype can be anything that takes a physical form—be it a wall of post-it notes, a role-playing activity, a space, an object, a model, an interface, or even a storyboard. You need to learn. Solve disagreements. Start a conversation. Fail quickly and cheaply. But still manage the solution-building process.
Test: Testing is the chance to get feedback on your solutions, refine solutions to make them better, and continue to learn about your users. Prototype as if you know you’re right, but test as if you know you’re wrong. You test to refine your prototypes and solutions, to learn more about your user, with the goal of testing and refining your POV.
Conclusion
Design thinking and innovation are critical to any business product development and strategy-making process. It’s also helpful for personal life and personal mission design. By adopting a design thinking approach, we can create solutions tailored to the user’s needs and preferences, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and better business outcomes. This approach offers numerous benefits, including increased creativity and innovation, improved customer experience, cost savings, and competitive advantage.