Other Parts of This Series:
- Part 3: Let’s Feel Programming Fundamentals - Part 3 (Condition, Loop)
- Part 5: Let’s Feel Programming Fundamentals - Part 5 (Procedural, Functional, OOP Style)
Function

C++ Condition & Loop (Photo Credit: Software Testing Help)
Story
In recent years, the world experienced many disasters. One of them is Covid-19 virus. Many people died all over the world until the vaccine invented. After a year of trying and dedication, scientist able to invented the vaccine. Many pharmaceutical companies discovered vaccines based on their own formula and all of the formulas are different from each other. Now company are going for production of vaccine. They set up their own factory and load the machine with their formula. Now workers supply the ingredients for the vaccine to the machine and machines produce the vaccine based on their formula. Those machine works in 2 ways.
- Point 1, in some machine workers supply the ingredients and supplied ingredients just used and not modified its original values.
- Point 2, in some machine workers supply the ingredients and supplied ingredients not just used but also modified its original values.
Function
In programming function is nothing but a factory/machine. That means, function is a predefined block of instructions that can produce something or some result. A function is simply a “chunk” of code that you can use over and over again, rather than writing it out multiple times. Functions enable programmers to break down or decompose a problem into smaller chunks, each of which performs a particular task. In the above story the factory’s machine are the example of function and their job is creating vaccine as function result.
According to tutorials point website “A function is a block of organized, reusable code that is used to perform a single, related action. Functions provide better modularity for your application and a high degree of code reusing.”
Basically function can be 2 types based on parameter value manipulation. They are:
- Pass By Value: Pass by value in a function is nothing just declare a function that dealing with only the value of parameter and not change the value of its original reference of the parameter. In this mechanism function expects value and caller pass the value and done. Point 1, is an example of pass by value. Here original parameter value is not changing.
- Pass By Reference: Unlike pass by value, it also dealing with the address or reference of the original parameter. If the parameter value is changing into the function than original parameter value is also change. So it can be called as binding the original parameter to the function. Point 2, is an example of pass by reference.
Pointer
C++ Condition (Photo Credit: Study.com)
Story
There is a company named X. Ashik is the human resource (HR) manager of the company. He manages the employee resource. He allocates the salary of an employee based on the employee’s position and type. Suppose a junior engineer gets 20000 taka, an associate engineer gets 40000 taka, a senior engineer gets 80000 taka, and so on. In this company, there is another special type of employee, supposed to be the lead engineer, and their job is to take care of the other types of employees. As they directly work with other juniors, the decision of the lead is also referred to as the juniors’ decision.
Memory Management/Allocation
Our computer memory can be considered as a collection of bytes. Byte is the 2nd smallest unit of computer memory. The 1st smallest unit of memory is a bit. When we write a program and run it, then the operating system starts allocating the memory based on the data type we used in the program. Like char type is 2 bytes, int type is 4 bytes, double is 8 bytes, and so on.
In the above story, Ashik is like our operating system, whose job is allocating resources based on employee type. And different types of employees can be considered as different data types, and they get different resources.
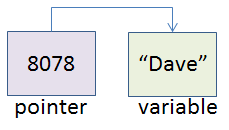
Pointer
A pointer in programming, is nothing but a special type of data that can hold the memory address of other data. That means a pointer can point to other data and hold the reference of that data. As a pointer holds the reference, any change in that data by that data or by the pointer reflects in both of them.
In the above story, the lead engineer can be considered as a pointer type, who points to the other junior engineer. And any decision by the lead or juniors is considered same decisions, as the lead holds reference to the juniors.
Variable Scope
C++ Condition (Photo Credit: Tech Vidvan)
Story
Jishan and Adnan are two childhood friends. They maintain a very healthy friendship despite having opposite characteristics. Opposite characteristics mean Jishan is a very polite, honest, and calm person, but Adnan is a dishonest and jolly person.
- Point 1: Now, as Jishan is an honest guy, he maintains only one girlfriend called Rina, and she wants him for his whole lifetime. Wherever Jishan goes, he takes the same girlfriend, Rina, who is the one and only girlfriend of his. Jishan called Rina a global lifetime girlfriend.
- Point 2: On the other hand, Adnan is a playboy-type guy. He maintains many more girlfriends called Ena, Mina, Tina, and more. Wherever Adnan goes he flirts with a new girl and impresses him and breaks up the relationship when he leaves the place. Adnan called them local one-time girlfriends.
Variable Scope
The scope of a variable means the accessibility of the variable in a particular area of the program, often called a block of code. In simple words, in a program, in which area a variable is accessible, that area is considered as the scope of that variable.
Some variable is declared as a global variable and this variable is accessible for the whole program. In the above story at point 1, Rina is an example of a global variable, and she is for Jishan’s whole life.
And some variable is declared as the local variable that is only for a block of code. Those variables are not accessible outside the block. Because after the block, those variables no longer exist. In the above story at point 2, Ena, Mina, Tina, and more are examples of local variables, and after Adnan leaves the place, those girlfriends and relationships are no longer accessible.
Variable Lifetime
The lifetime of a variable is defined as for how much time period a variable is occupying a valid space in the system’s memory, or the lifetime is the period between when memory is allocated to hold the variable and when it is freed. Once the variable is out of scope, its lifetime ends.
In the above story at point 1, Rina has a lifelong relationship with Jishan. That means a global variable created with the program starts and is destroyed with the program’s end.
In the above story at point 2, Ena, Mina, Tina, and more have a short lifetime or local scope, one-time relationship with Adnan. After Adnan leaves the place, their onetime relationship is being destroyed.
Code Example (C++)
| |
Insha Allah, in the upcoming blogs we will deep dive other fundamental concepts. Until than, may Allah keep you healthy and happy.