Other Parts of This Series:
- Part 4: Let’s Feel Programming Fundamentals - Part 4 (Function, Pointer, Scope)
- Part 6: Let’s Feel Programming Fundamentals - Part 6 (Data Structure)

Procedural, Functional & Object Oriented Programming (Photo Credit: Empower Youth)
Story
Amit, Atik and Mithun are three close friends. They all like programming. But their thinking approach is quite different when they program. They think each in below different style:
- Point 1: Amit thinks everything in the program is a collection of variables. Means program contains data and functions (represent action). And based on this action, produces some result. He keeps those things separate from each other but use both.
- Point 2: Atik thinks everything as function. He treat function as variable thus use it everywhere. He also thinks that everything should be like machine (function) and should take input and produce output and no modification of existing. No side effect and maintain immutability.
- Point 3: Mithun thinks in a different way. He tries to compare everything to a real-world object. He tries to combine the property and behavior together in a common place. He believes everything is an object, and every object has one or more properties, like data and behavior (variable and functions). For example, a person is an object that has some property like weight, height, color, etc., and some behavior, like a person can walk, talk, eat, etc.
Procedural Programming
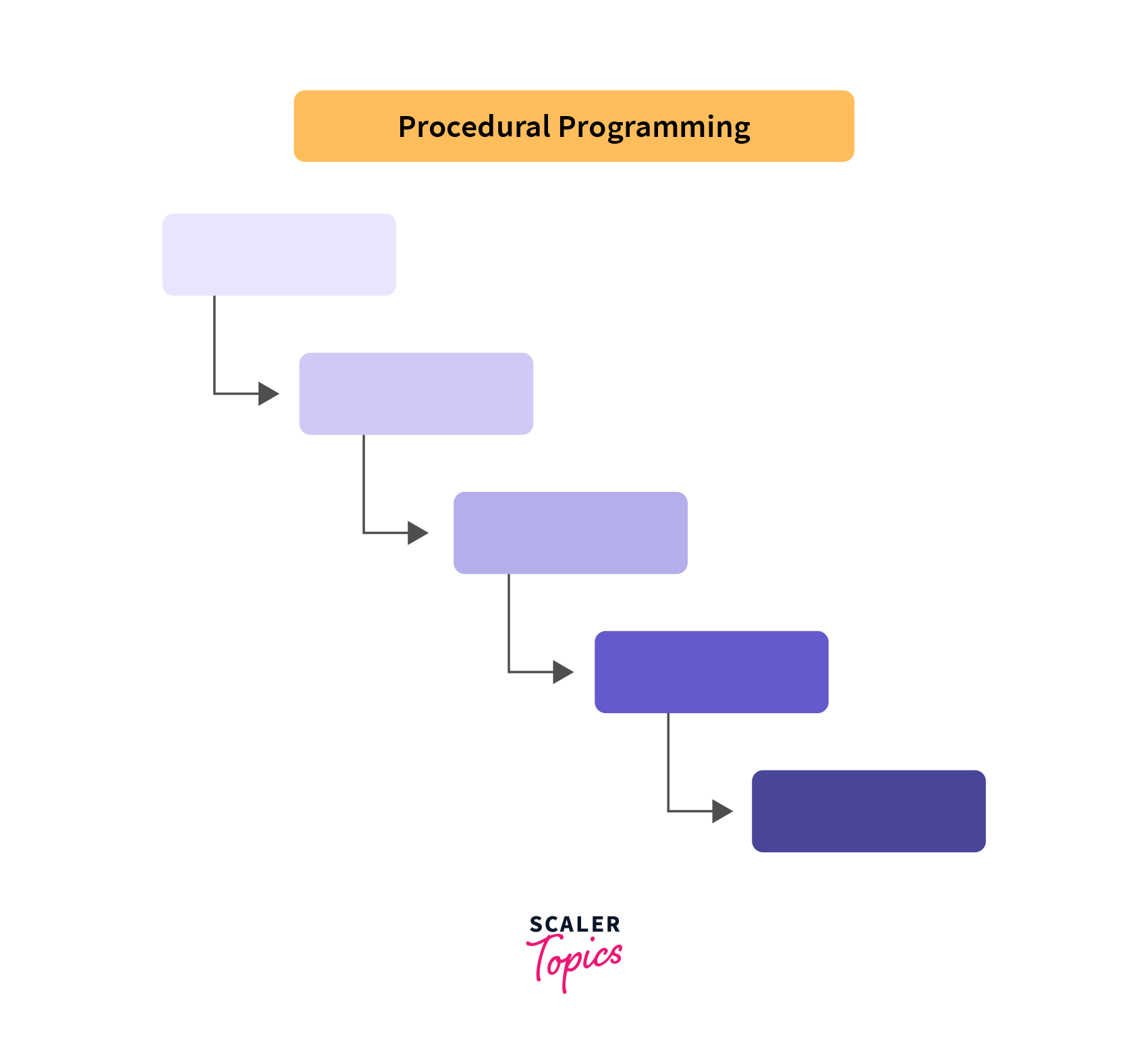
Procedural Programming (Photo Credit: Scaler Topics)
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm where focuses on procedures or routines (functions). Data and functions are separate. Procedures contain sequence instructions that specify a computational step carried out upon execution. What this means? It means in procedural programming, instruction declared top down approach using variable (data) & function (routine) and they execute also top dowm manner step by step as you see in the picture.
In the above story at point 1, Amit’s thinking approach is a procedural programming approach.
Functional Programming
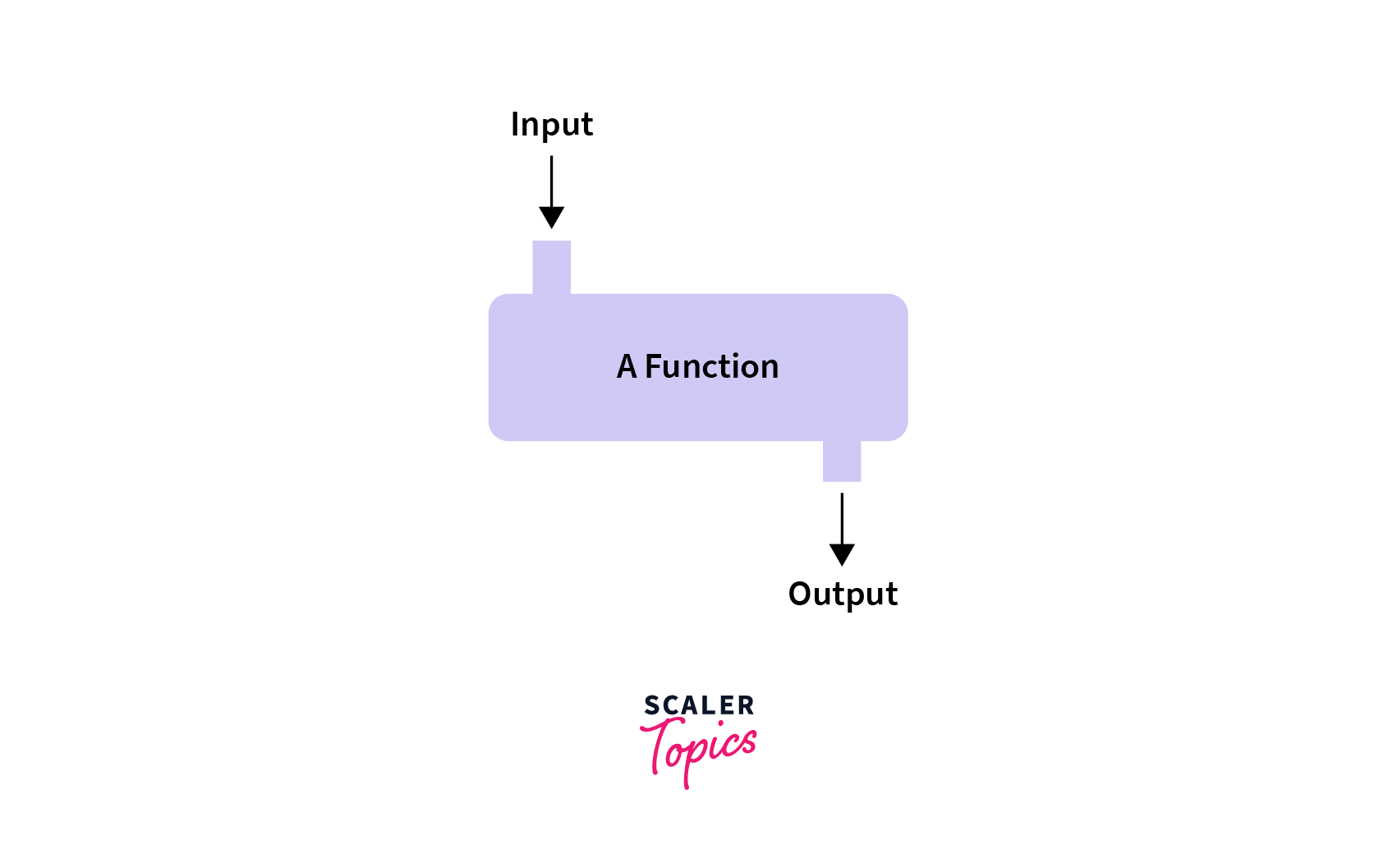
Functional Programming (Photo Credit: Scaler Topics)
Functional programming is a programming paradigm where everything is thought of as a function. In functional programming, a program is made modular by separating the concerns into different functions. And data is being passed as parameters, and based on the parameter and its value, the function produces a result. Function is pure here and treat as variable and can pass as perameter of other function as well. A big program is working by chaning of different functions in this paradiagram. F#, Scala, Julia, R etc. are the functional programming language.
In the above story at point 2, Atik’s thinking approach is a functional programming approach.
Object Oriented Programming (OOP)
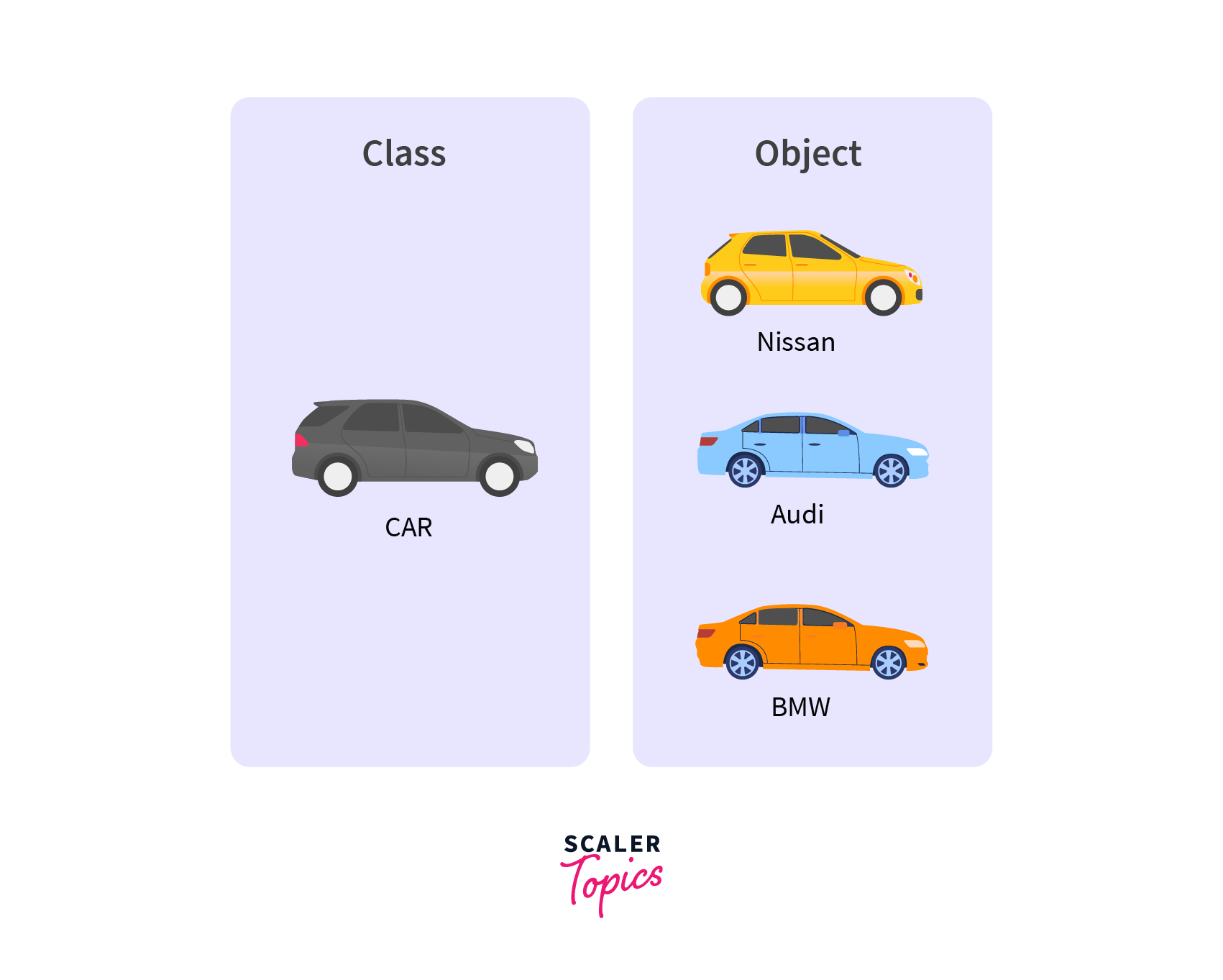
Object Oriented Programming (Photo Credit: Scalar Topics)
Object oriented programming, in short OOP is a programming paradigm where everything is considered as a real life object. Here a whole program is a composition of a lot of different classes and objects. Programs are also being modular by class and its object. Objects talk to each other to perform the task.
In the above story at point 3, Mithun’s thinking approach is OOP approach.
Theoretically there are 7 pillars of OOP. They are:
- Class: Class is a blueprint / template definition / signature of an object. It can be considered as the data type of an object.
- Object: Object is the data of a class type. It is the raw value that signature by a class.
- Property and methods: Property is the data that represents an object and methods is the function that represents object behavior.
- Encapsulation: Encapsulation in OOP is the concept of hiding the confidential data into an object. It makes sure only the owned object can access the confidential data.
- Abstraction: Abstraction is a process for hiding the unnecessary implementational details and provides a high level access control of the objects.
- Inheritance: Inheritance means getting some data and behaviors from the parents. In OOP the child class can inherit the parent class data and behavior by it.
- Polymorphism: Poly means many and morphism means type. That means many types. We can achieve many types of single things by the polymorphism principle.
Code Example (C++)
Procedural
Functional (Though C++ is not pure functional but support functional using lambda)
OOP
Insha Allah, in the upcoming blogs we will deep dive other fundamental concepts. Until than, may Allah keep you healthy and happy.