Other Parts of This Series:
- Part 1: All About Software Engineering: Part 1 (Science, Engineering and Mindset Part)
- Part 3: All About Software Engineering: Part 3 (Involved Parties At Different Stages Of SDLC)
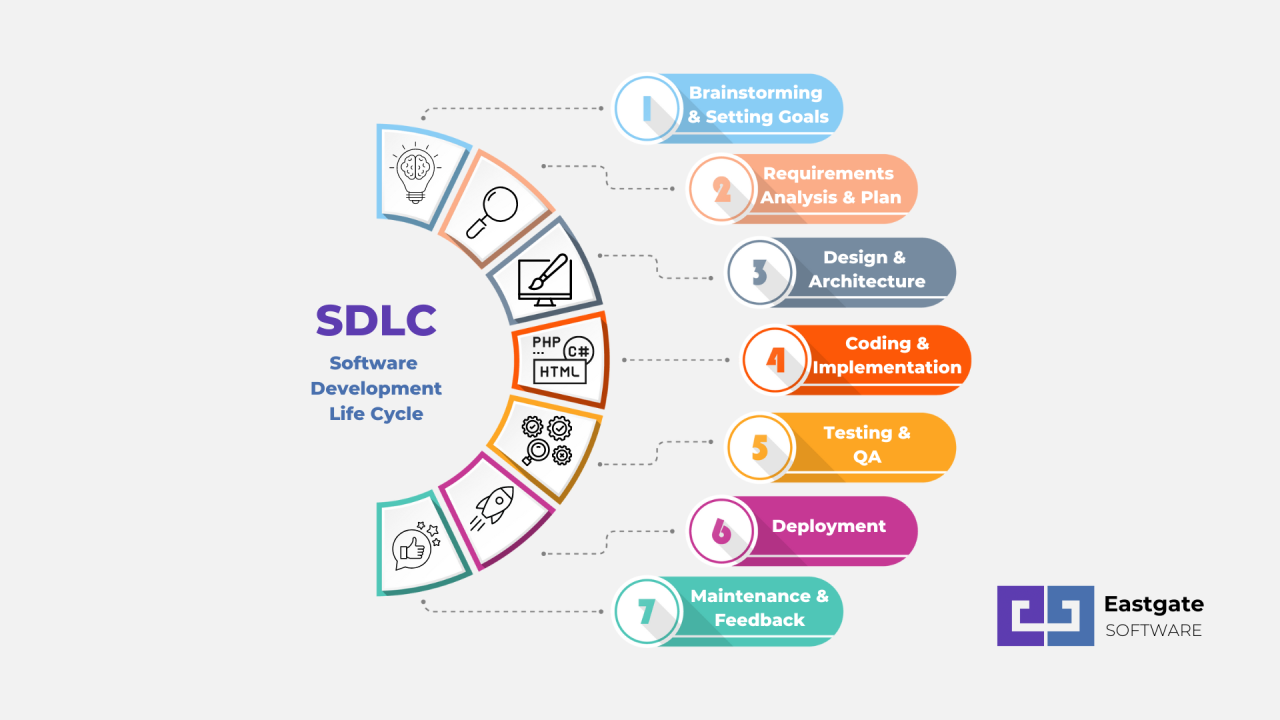
Software Development Life Cycle (Photo Credit: Eastgate Software)
In this series, we try to explore software engineering in a modern way. We will try to learn the different software engineering aspects one by one. In this part, we try to explore the software development life cycle (SDLC).
So let’s get started…
Story
After evaluating the essential science, engineering, and mindset shifting for successful software production, Shuvo and Tapu want to explore the steps to follow for software creation. They are now in search of the software life cycle and the ideal process for efficient and smooth software building.
What is SDLC?
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) can be considered as a framework for the software development teams, which refers to the critical stages of the process of developing software applications (from planning and coding to maintaining, etc.). The SDLC involves several phases that allow teams to break down complex projects into manageable tasks.
Thus, adhering to the SDLC ensures that software is developed in a systematic and organized way, minimizing errors and reducing the risk of project failure. By following the SDLC, software development teams can produce high-quality software products that meet the needs of their clients/customers.
Phases of SDLC:
There are several stages involved in SDLC. Team-wise it can be modified as well based on the team and project’s needs. But in general we can define the SDLC in the following 7 stages:
- Brainstorming & setting goals: This is the early stage of the software development. Business objectives and goals are determined at this early stage, along with any specifications or needs that could be necessary for a successful project conclusion. At this point, it’s also important to think about any risks involved in reaching these objectives.
- Requirement analysis & planning: Once the business objectives and goals are determined, then the requirements need to be gathered from different parties and analyzed for a successful software system. Also need solid planning too for further processing. This phase aims to define the functionality, features, and constraints of the software system to be developed.
- Design & architecture: From this stage, technical parts begin. In this phase, the system architecture and design are planned based on the requirements gathered in the previous phase. Design decisions include selecting appropriate technologies and defining the system’s structure, interfaces, modules, and data architecture.
- Coding & implementation: This is the part where actual coding or implementation is done based on the architecture design. Writing code, testing code, and integrating code are the parts of this phase.
- Testing & QA: The testing phase verifies that the software meets its requirements, functions correctly, and performs reliably under various conditions. Testing activities include unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing. Test cases are designed, executed, and evaluated to identify defects and ensure quality.
- Deployment: Once the software has been tested and validated, it is ready for deployment to production or end-users. Deployment involves installing, configuring, and distributing the software to the target environment, ensuring a smooth transition from development to production.
- Maintenance & feedback: The maintenance phase involves ongoing support, monitoring, and maintenance of the software after deployment. This includes bug fixes, updates, enhancements, and optimizations to address issues, improve performance, and adapt to changing requirements over time.
What is Software Process?
We can summarize the software process as a set of activities whose goal is the development or evaluation of the software. Basically there are 4 fundamental process activities involved in all common software processes. They are:
- Software specification: define what to produce in between a specified boundary.
- Software development: design and program the software.
- Software validation: test and validate the developed software.
- Software evaluation: get and adopt feedback in the software.
What is Software Process Model?
A software process model is a structured approach used to define, organize, and manage the activities involved in software development. It provides a framework for planning, executing, and monitoring the software development process from initiation to completion.
A software process model may include the workflow model, data flow model, activity model, and action/role model.
Different Software Process Models:
The software process model is something that can vary or not be a universal rule that must be followed. A company, organization, or team can change or use their own modified format of the process model.
But some of the well-established generic software process models are as follows:
Waterfall Model Waterfall Software Process Model (Photo Credit: bap-software)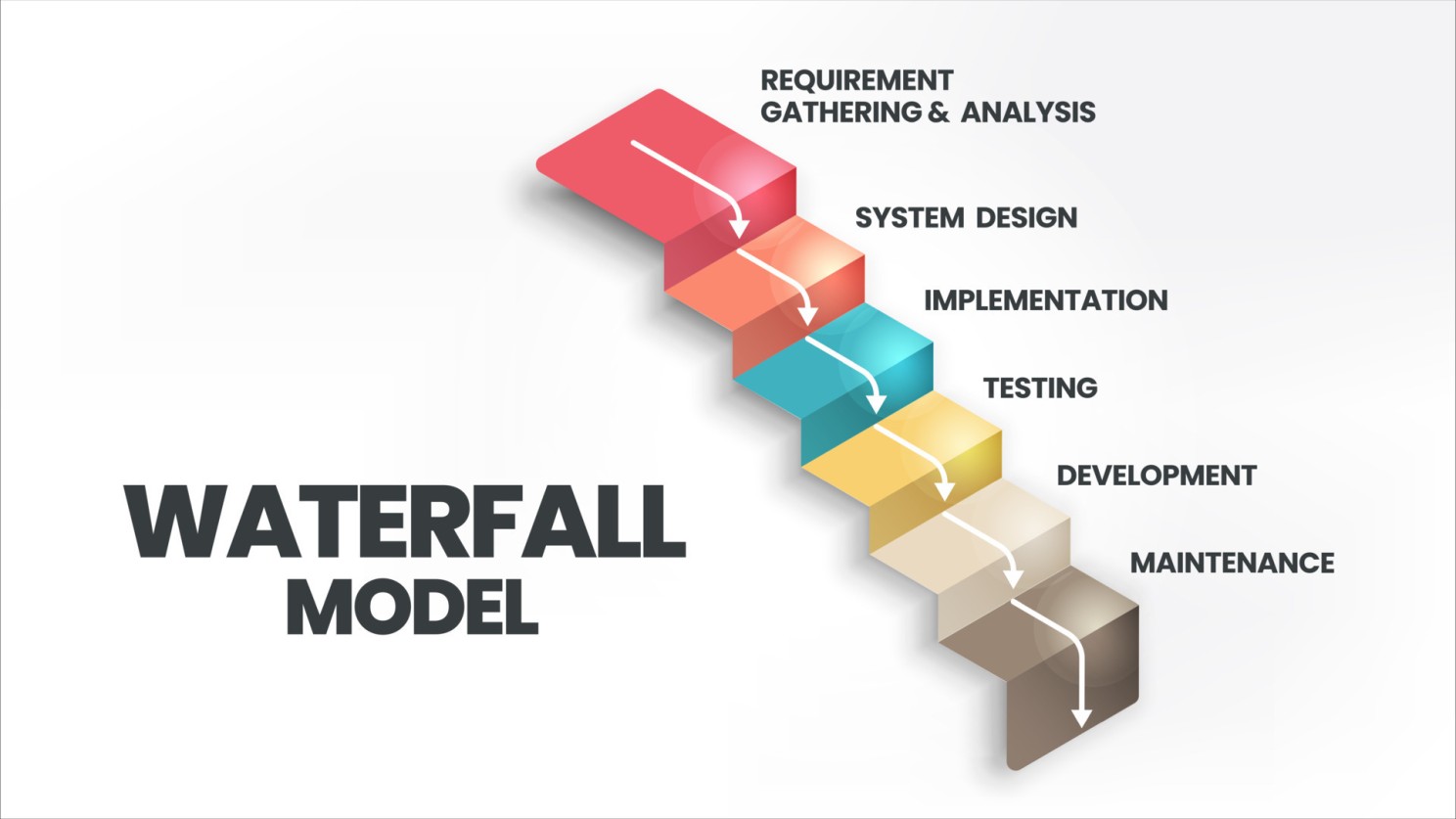
- The waterfall model follows a linear, sequential approach to software development, where each phase (requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment) is completed before moving on to the next.
- Progress flows downward like a waterfall, with distinct phases and well-defined deliverables.
- This model is suitable for projects with stable requirements and a clear understanding of the end product.
Iterative Model Iterative Software Process Model (Photo Credit: reasearchgate)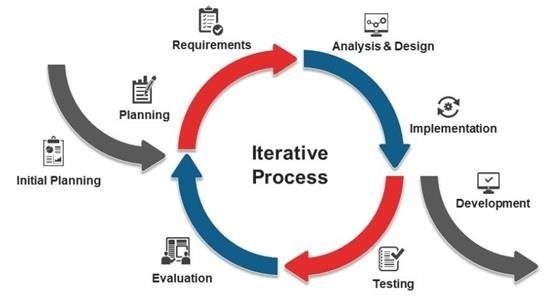
- The iterative model divides the software development process into smaller iterations or cycles, each consisting of phases such as planning, requirements analysis, design, implementation, and testing.
- Each iteration results in a working version of the software that can be reviewed, refined, and enhanced in subsequent iterations.
- Iterative models allow for flexibility, adaptability, and incremental development, making them suitable for projects with evolving requirements or complex systems.
Incremental Model Incremental Software Process Model (Photo Credit: guru99)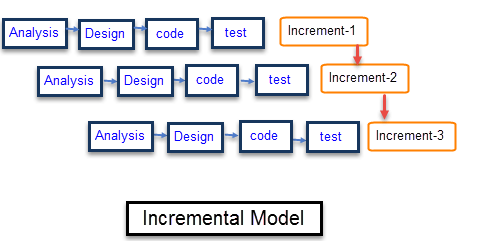
- The incremental model builds upon the iterative approach by dividing the software development process into multiple increments or releases.
- Each increment adds new features or functionality to the software, gradually expanding its capabilities over time.
- Incremental models enable stakeholders to receive early and frequent deliveries of the software, facilitating feedback and validation throughout the development process.
Spiral Model Spiral Software Process Model (Photo Credit: wikipedia)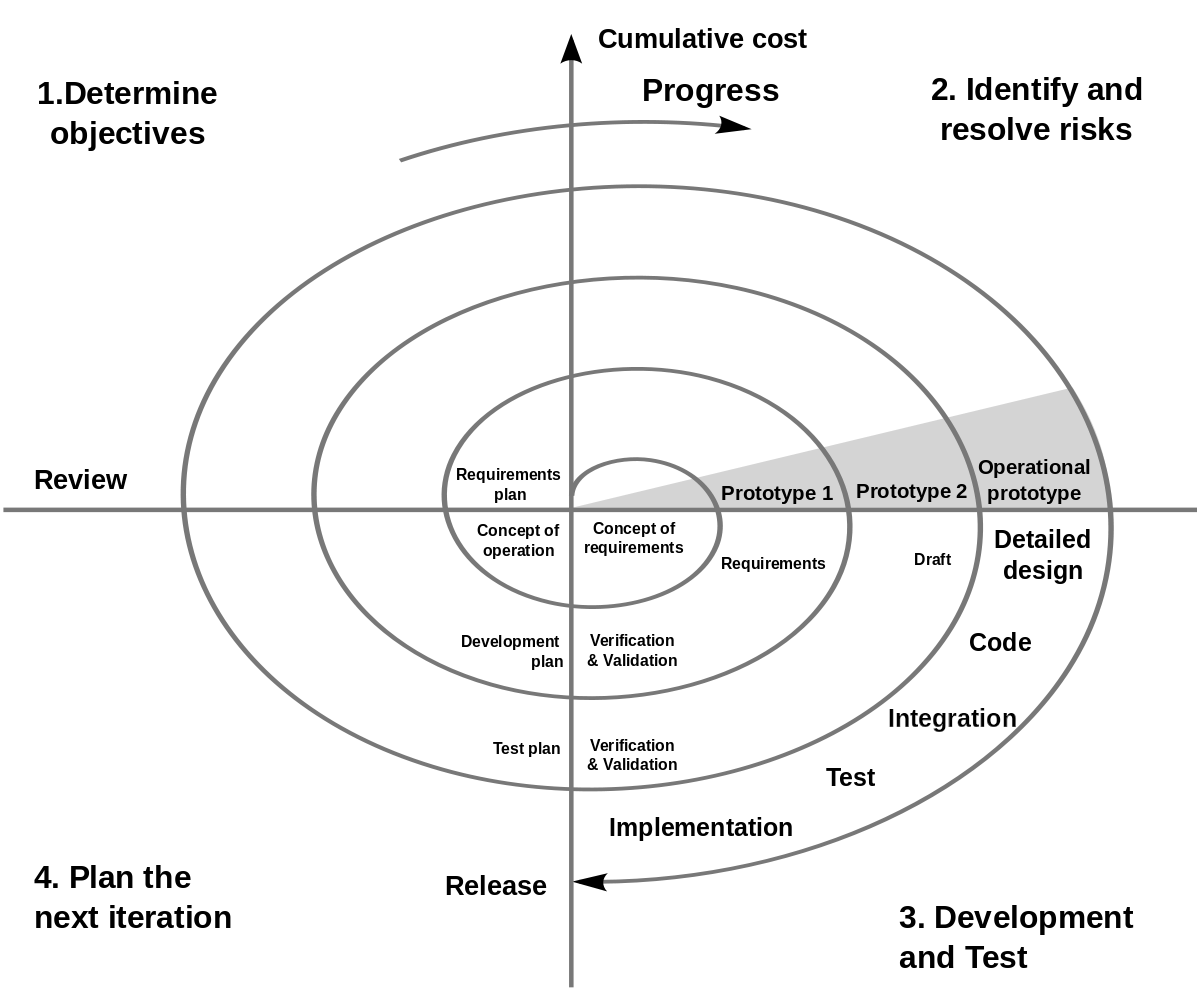
- The spiral model combines elements of both iterative and waterfall approaches, incorporating risk analysis, prototyping, and iterative development cycles.
- It consists of multiple loops or spirals, each representing a phase of the software development process (e.g., planning, risk analysis, prototyping, evaluation).
- The spiral model is particularly suitable for projects with high levels of uncertainty, where risk management and early validation are critical.
Agile Model Agile Software Process Model (Photo Credit: javaTpoint)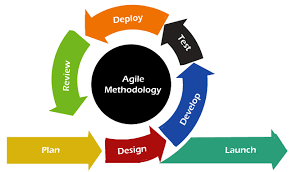
- Agile methodologies, such as Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP), emphasize collaboration, flexibility, and customer involvement in software development.
- Agile teams work in short iterations called sprints, delivering small, incremental improvements to the software in response to changing requirements and feedback.
- Agile models prioritize individuals and interactions over processes and tools, embracing change and continuous improvement to deliver high-quality software efficiently.
From the above generic model, agile model or agile methodology is the most modern and well used software process model in modern days software development.
Summary:
So understanding the software development life cycle (SDLC) and all its stages is crucial for the development of efficient working software. Choosing and practicing the right software process model based on the nature of your software project is also important for success.